Overview
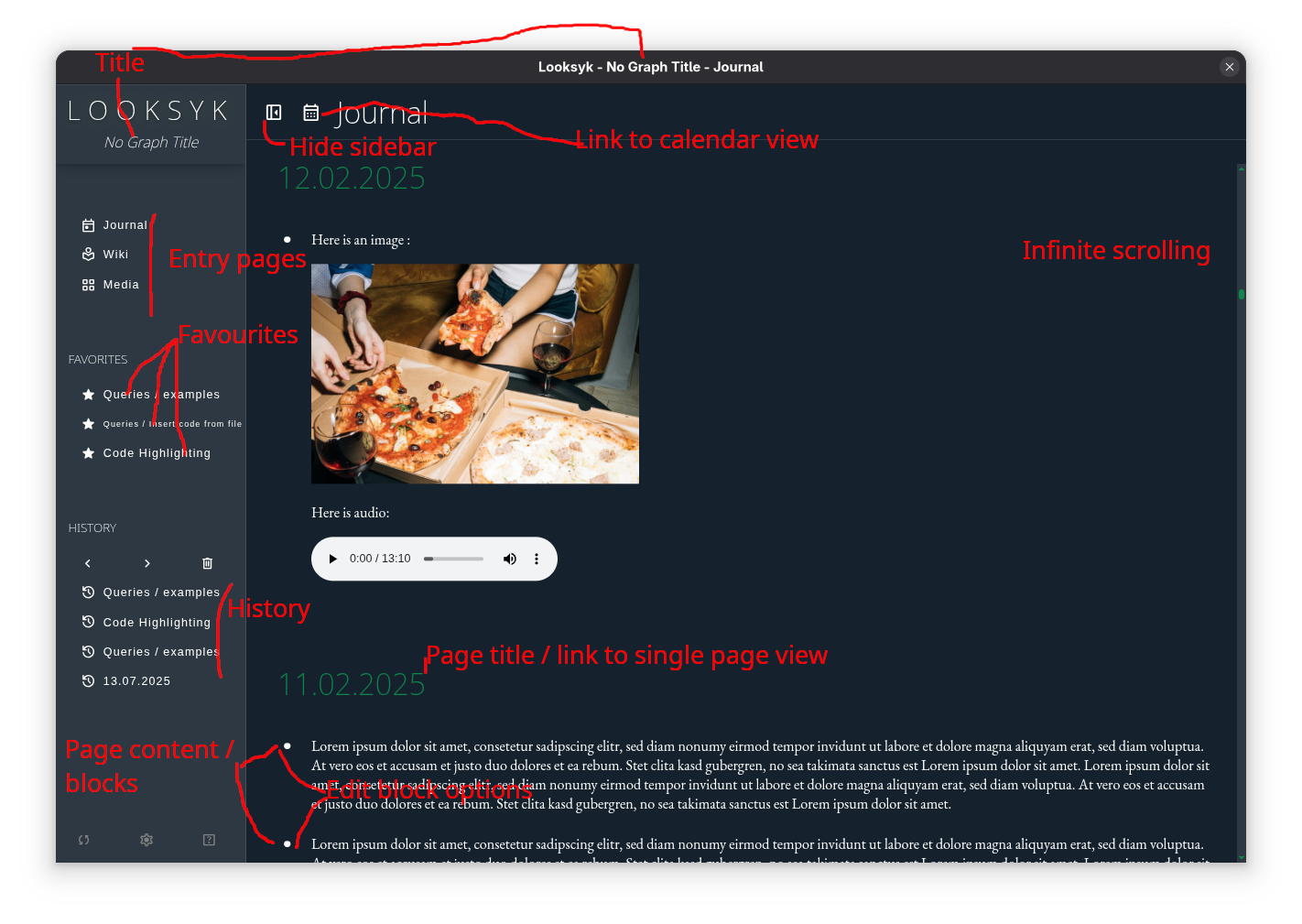
Overview of Looksyk's basic features in the Journal view.
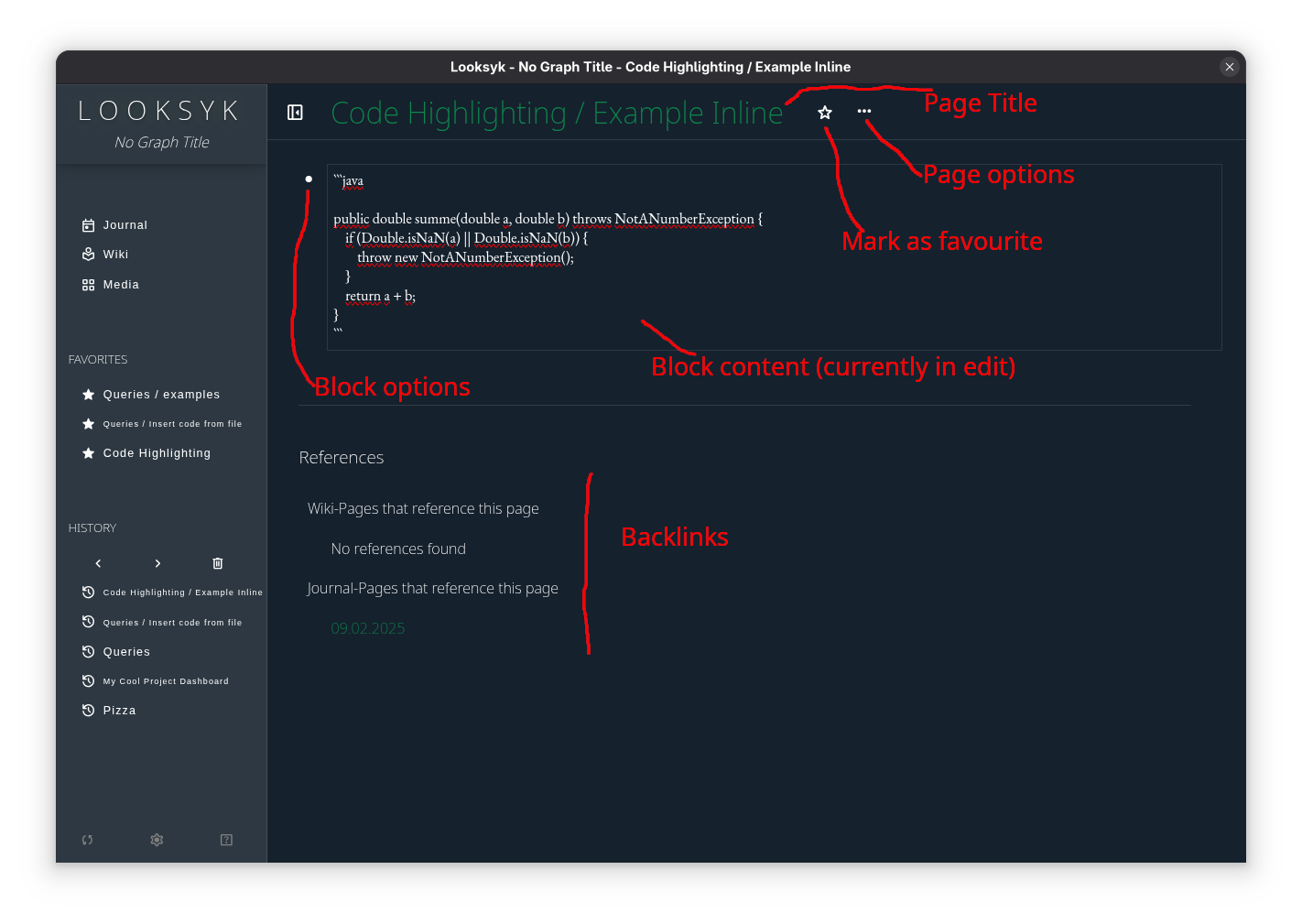
Overview of Looksyk's basic features in the Page view.
Detailed Usage Instructions
For detailed instructions on how to use Looksyk, please refer to the following sections:
Configuration
Settings and customization options for Looksyk.
Data Storage
How and where data is stored.
Design
Customizing appearance and layout.
Markdown & Syntax & Keyboard Shortcuts
Supported markdown features and syntax details.
Queries
How to use queries to filter and find information.
Boards
Use your existing markdown blocks as cards on a custom (kanban-)board
Templates
Using and creating templates for your notes.
